Advanced traffic shifting📜
In this lab, we will learn how to use request properties to route the traffic between multiple service versions.
Let’s enable automatic sidecar injection on the default namespace by adding the label istio-injection=enabled:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
Check that the default namespace contains the label for Istio proxy injection.
kubectl get namespace -L istio-injection
default Active 19h enabled
kube-system Active 19h
kube-public Active 19h
kube-node-lease Active 19h
flux-system Active 19h
bigbang Active 16h
jaeger Active 16h enabled
gatekeeper-system Active 16h
istio-operator Active 16h disabled
logging Active 16h enabled
monitoring Active 16h
kiali Active 16h enabled
istio-system Active 16h
eck-operator Active 16h
Next, we will deploy the Web Frontend, Customers v1, Customers v2, and the corresponding VirtualServices and DestinationRule. Once everything is deployed, all traffic will be routed to the Customers v1.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: web-frontend
labels:
app: web-frontend
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: web-frontend
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: web-frontend
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: gcr.io/tetratelabs/web-frontend:1.0.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: web
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: CUSTOMER_SERVICE_URL
value: 'http://customers.default.svc.cluster.local'
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: web-frontend
labels:
app: web-frontend
spec:
selector:
app: web-frontend
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
targetPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: web-frontend
spec:
hosts:
- 'frontend.bigbang.dev'
gateways:
- istio-system/public
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: web-frontend.default.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
Save the above YAML to web-frontend.yaml and create the deployment and service using kubectl apply -f web-frontend.yaml.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: customers-v1
labels:
app: customers
version: v1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: customers
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: customers
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: gcr.io/tetratelabs/customers:1.0.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: svc
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: customers-v2
labels:
app: customers
version: v2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: customers
version: v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: customers
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- image: gcr.io/tetratelabs/customers:2.0.0
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: svc
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: customers
labels:
app: customers
spec:
selector:
app: customers
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
targetPort: 3000
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: customers
spec:
hosts:
- 'customers.default.svc.cluster.local'
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: customers.default.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v1
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: customers
spec:
host: customers.default.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
Save the above YAML to customers-v1-v2.yaml and create the resources with kubectl apply -f customers-v1-v2.yaml.
To reach the host
frontend.bigbang.dev, it is necessary to add the following line in /etc/hosts:<public-ip> frontend.bigbang.devAdditional Step for WSL users📜
Using WSL requires users to update both their Windows Hosts File with the cluster IP as well as updating the
/etc/hostsfile on WSL.PowerToys - It is recommended to install the PowerToys application to update your Windows Hosts File using the Host File Editor. * After opening PowerToys, navigate to
Host File Editorand update the IP field for<package>.bigbang.dev* If the<package>.bigbang.devfield does not exist, create<package>.bigbang.devfor each package you are using, or plan to open on the web, then apply the cluster IPAlternative to using PowerToys:
Open Notepad or another text editor like Notepad++
In the text editor, select File > Open and open the HOST file location at
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\.Select Text Documents (*txt) in the bottom-right of the Open window and change it to All Files.
When files appear in the folder, double click hosts to open it.
Edit the HOSTS file and update the IP field for
<package>.bigbang.dev5a. If the
<package>.bigbang.devfield does not exist, create<package>.bigbang.devfor each package you are using, or plan to open on the web, then apply the cluster IPSave your changes
To ensure everything is deployed and works correctly, open the frontend.bigbang.dev and ensure we are getting the responses back from the Customers v1. we should only see the NAME column in the response.
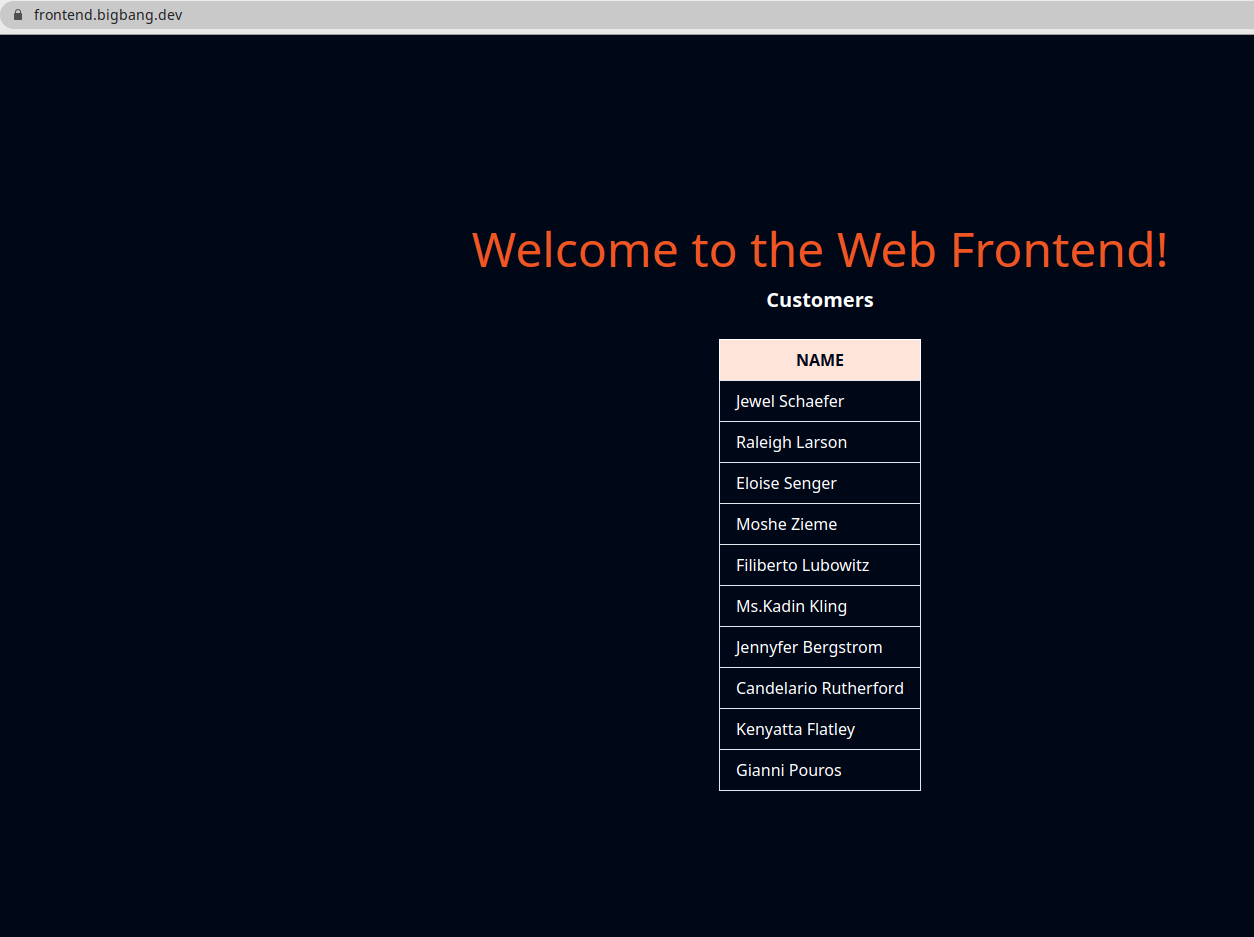
We will update the customers VirtualService and update how the traffic is being routed between two versions of the customers service.
Let’s look at a YAML that routes the traffic to Customers v2, if the request contains a header user: debug. If the header is not set, we are routed to the Customers v1.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: customers
spec:
hosts:
- 'customers.default.svc.cluster.local'
http:
- match:
- headers:
user:
exact: debug
route:
- destination:
host: customers.default.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v2
- route:
- destination:
host: customers.default.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
subset: v1
Save the above YAML to customers-vs-split.yaml and update the VirtualService with kubectl apply -f customers-vs-split.yaml.
The destinations in the VirtualService would also work if we didn’t provide the port number. That’s because the service has a single port defined.
If we open frontend.bigbang.dev, we should still get back the response from the Customers v1. If we add the header user: debug to the request we will notice that the customers’ response is from the Customers v2. We can use the ModHeader extension to modify the headers from the browser:
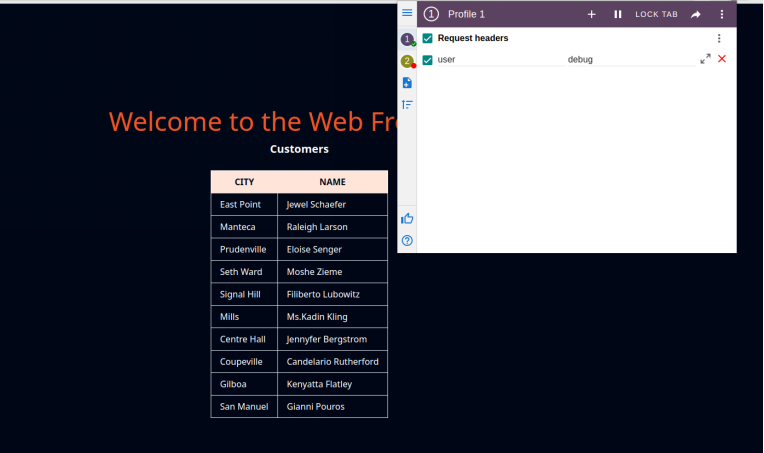
Alternatively, we can use cURL and add the header to the request like this:
curl -H "user: debug" https://frontend.bigbang.dev/
...
<tr>
<td class="border px-4 py-2">San Manuel</td>
<td class="border px-4 py-2">Gianni Pouros</td>
</tr>
...
if the header user: debug is not used, only the name is observed:
curl https://frontend.bigbang.dev/
...
<tr>
<td class="border px-4 py-2">Gianni Pouros</td>
</tr>
...
Clean-up📜
The following commands will clean-up your cluster.
Delete the the service, deployment and virtual service of customer and web-frontend.
kubectl delete -f web-frontend.yaml
kubectl delete -f customers-v1-v2.yaml